EVM-Deep-Dives
Ethereum Virtual Machine 以太坊虚拟机,处理智能合约Smart Contract, 当Transaction送到Node后,Node内的EVM会被create出来,完成Transaction任务,简单来说EVM是一个高阶程序在模拟一台电脑的运算。
Part 0 - Ethereum Contract ABI & EVM Bytecode
由于以太坊使用EVM(以太坊虚拟机)作为系统的核心,使用高级语言Solidity编写的智能合约代码需要编译成EVM字节码和合约ABI才能运行,在与智能合约交互时,需要先了解他们.
Bytecode & ABI
EVM Bytecode: EVM字节码是EVM上可执行的代码Contract ABI: ABI是与EVM字节码交互的接口
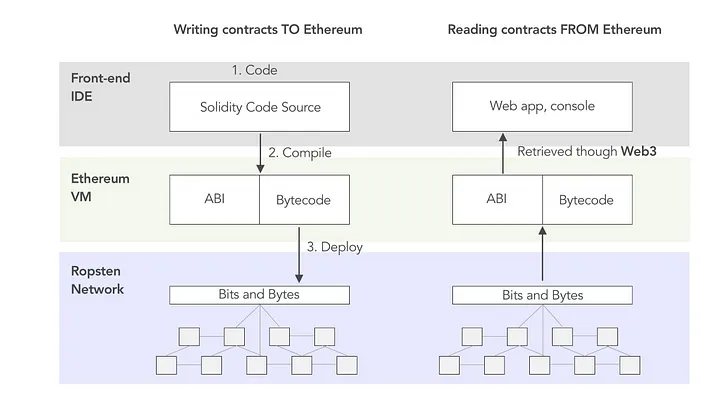
左边是编译过程,右边是交互过程
Part 1: - Solidity -> Bytecode -> Opcode
Part 3: - Storage
在以太坊虚拟机(EVM)中运行的每个智能合约都将状态保存在存储中,这个存储空间可以看作是一个很大的数组,初始化都为0,数组中每个值都是32bytes,智能合约可以读取或写入任意位置的值.在组成以太坊网络的物理计算机上,存储并不是这样实现的,存储空间非常稀疏,没有必要存储零,将32字节的键映射到32字节的值的键/值存储可以很好地完成工作。一个不存在的键被简单定义为映射到零值.
由于零不会占用任何空间,因此可以通过将某个值设置为零来回收存储空间.在智能合约中,如果你将一个值更改为零时,就可以获得Gas退款.
Understanding Ethereum Smart Contract Storage
智能合约存储是一个键值映射,它将一个32字节的键映射到一个32字节的值.
- 固定大小的变量(Fixed Size Variables)
- Slot Packing 插槽包装
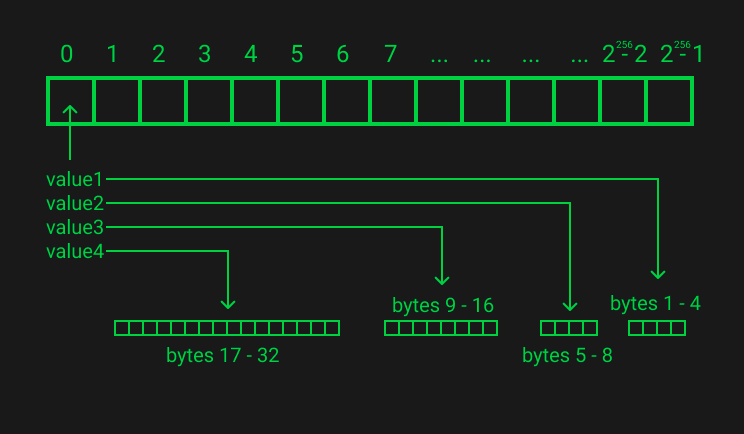
请注意,uint8时最小的实体类型,因此打包不能小于1字节(8位)
- EVM Storage Opcodes
- SSTORE
1 | |
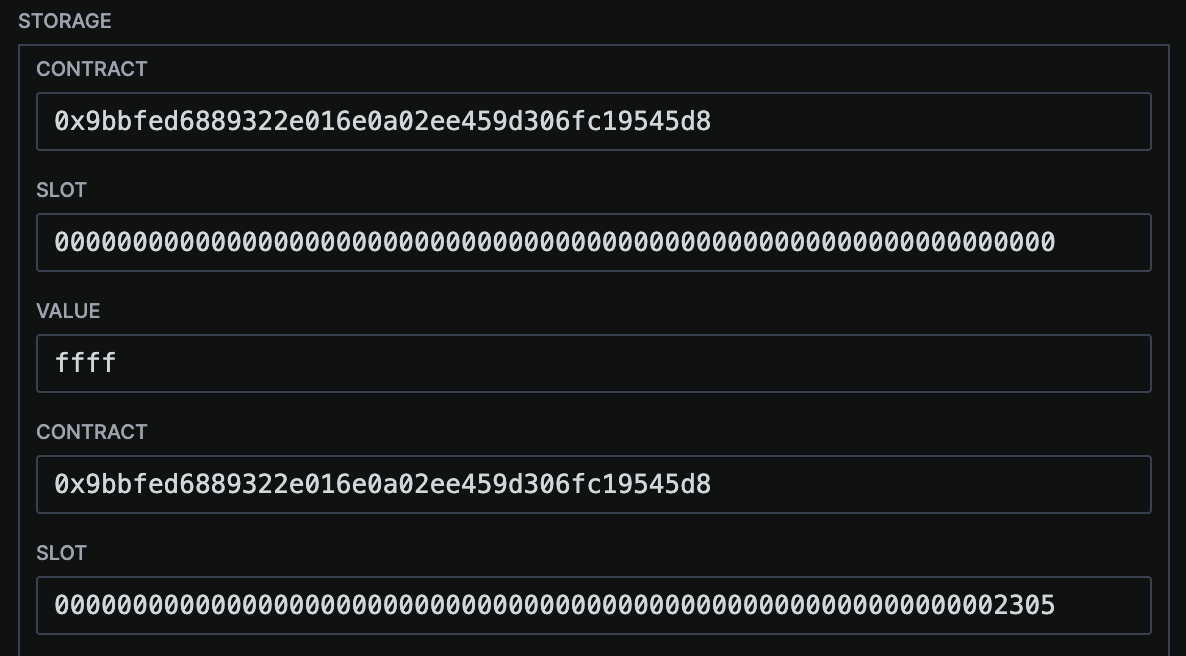
- SLOAD
1 | |
“World State” Storage
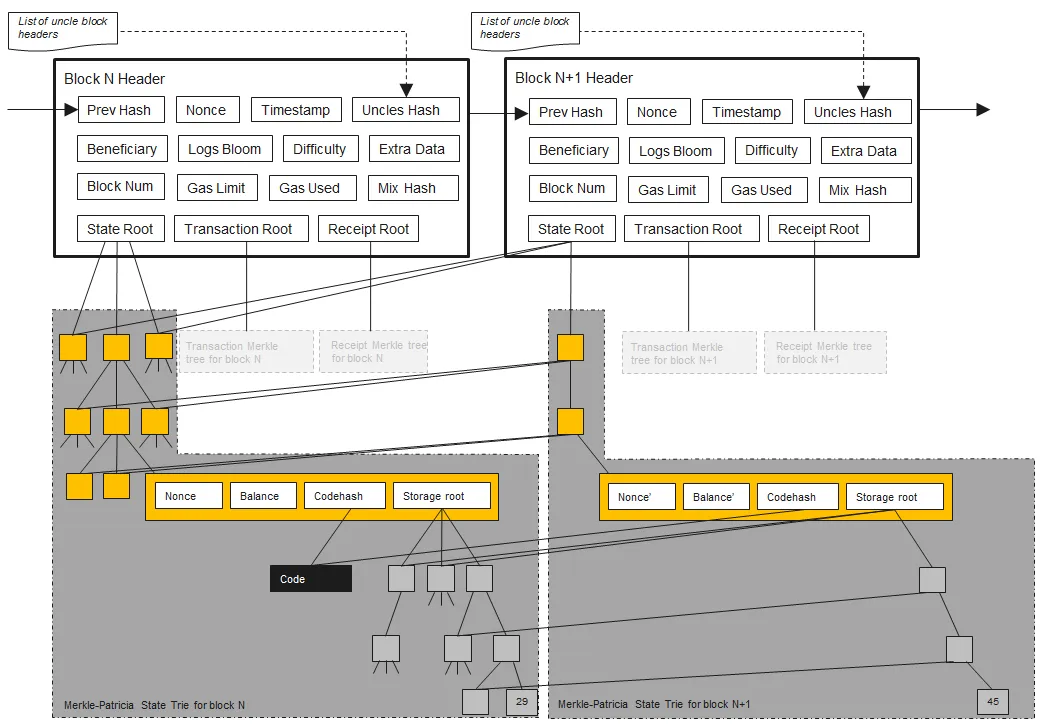
Block Header
The block header contains the following fields:
- ParentHash - Keccak hash of the parent block
- UncleHash - Keccak hash for uncled blocks
- Beneficiary(CoinBase) - Beneficiary address, mining free recipient
- State Root(Root) - Keccak Hash of root node of state trie (post-execution)
- Transaction Root(TxHash) - Keccak Hash of the root node of transaction trie
- Receipt Root(ReceiptHash) - Keccak Hash of the root node of receipt trie
- LogsBloom(Bloom) - Bloom filter of two fields, log address & log topic in the receipts
- Difficulty - Scalare value of the difficulty of the previous block
- Block Num(Number) - Scalar value of the number of ancestor blocks
- Gas Limit(GasLimit) - Scalar value of the current limit of gas usage per block
- Gas Used(GasUsed) - Scalar value of the total gas spent on transactions in this block
- Timestamp(Time) - Scale value of output of UNIX time()
- Extra Data(Extra) - 32 byte data relevant to this block
- Mix Hash(MixDigest) - 256-bit value used with a nonce to prove proof of work computation
- Nonce - Used in proof of work computation
State Root
状态根的作用类似于默克尔树中的Root,因为它是一个哈希值,取决于其下的所有数据块,如果任何数据片段发生变化,根也会随之变化.
- Merkle Root
1 | |
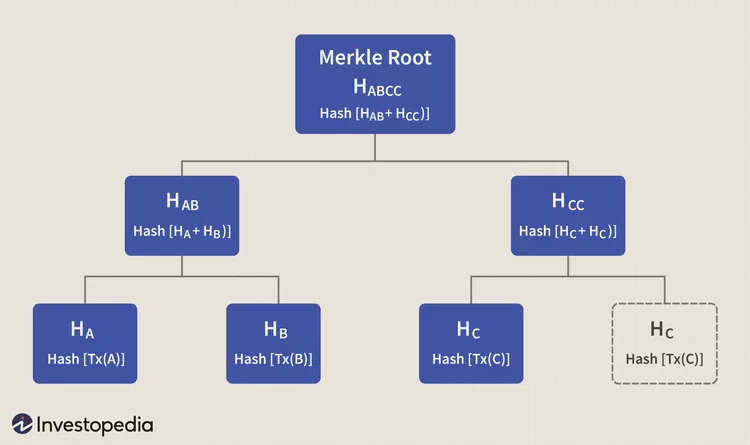
根称为默克尔根,它包含了区块上存在的每一笔交易散列的所有信息,它提供一个单点哈希值,可以验证该区块上的所有内容.
State Root的数据结构是默克尔树,它存储了网络上每个以太坊账户的键值对,其中键是以太坊地址,值是以太坊账户对象.
- Trie Data Structures | Merkle Trees
trie comes from retrieve, A trie is a tree-like data structure. Merkle tree’s primary purpose if to prove the consistency of data, and is essentially a tree of hashes.
“Merkle tree is a tree in which every leaf node is labelled with the hash of a data block and every non-leaf node is labelled with the cryptographic hash of the labels of its child nodes.”
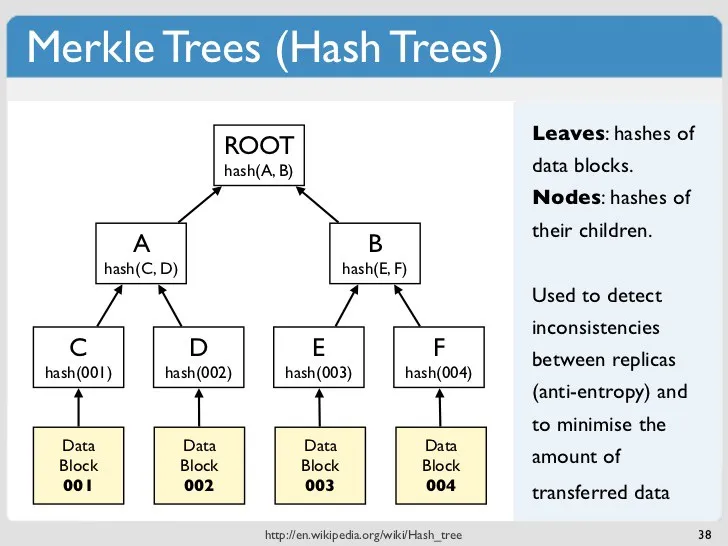
默克尔树的优势
1 | |
- Leveldb
Leveldb是一个开源的谷歌键值存储库
1 | |
- HP(Hex Prefixed) encoding
以太坊源码解析: state
以太坊源码解析: evm
参考资料
Ethereum EVM illustrated
EVM Source Code in go-ethereum
Runtime Example
What Is a Merkle Root
Understanding Trie Database in Ethereum
以太坊源码解析
以太坊源码解析